Quantum computing once felt like pure science fiction: machines that could explore vast possibilities all at once. Today, it’s becoming real. Governments, tech giants, and investors are pouring billions into the race to build the first truly useful quantum computer.
Some major players, like IBM and Google, are backing superconducting circuits, while IonQ and Quantinuum focus on trapped ions. But one Silicon Valley contender, PsiQuantum, is taking a different path. In September 2025, the company closed a US$1 billion Series E round at a US$7 billion valuation, backed by BlackRock, Temasek, Baillie Gifford, and new investors including NVIDIA’s NVentures.
These investors see PsiQuantum’s photonic approach as the most scalable route to a fault-tolerant, million-qubit quantum computer. By manufacturing quantum chips in standard semiconductor fabs and treating quantum hardware as an engineering and production challenge, PsiQuantum aims to deliver a utility-scale machine that many believe will define the next era of computation.
A Brief History
The origins of quantum computing can be traced back to the early 20th century when several groundbreaking discoveries in the field of quantum mechanics laid the foundation for this novel approach to computation. Key scientists, such as Max Planck, Albert Einstein, and Niels Bohr, contributed to the development of quantum mechanics, which would later provide the principles for quantum computing.
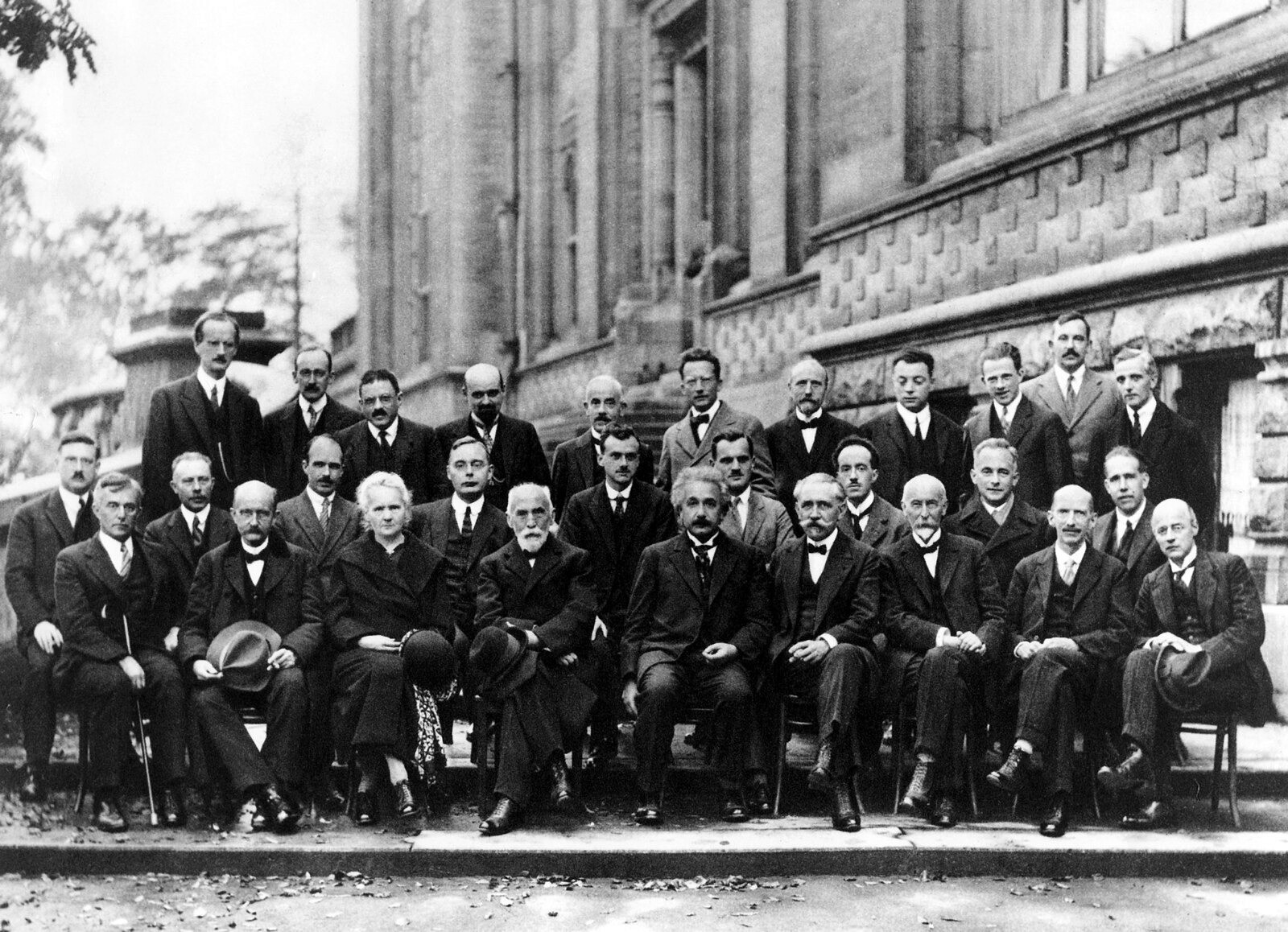

The fifth Solvay Conference in 1927. Photo Credit: Wikipedia.org
The ideas of quantum computers began in the 1980s, when physicist Richard Feynman showed that classical computers struggle to simulate quantum systems, suggesting that nature itself “computes” in a quantum way. In 1985, David Deutsch formalized the concept of a universal quantum computer, describing how quantum bits (qubits) could perform computations impossible for classical machines.
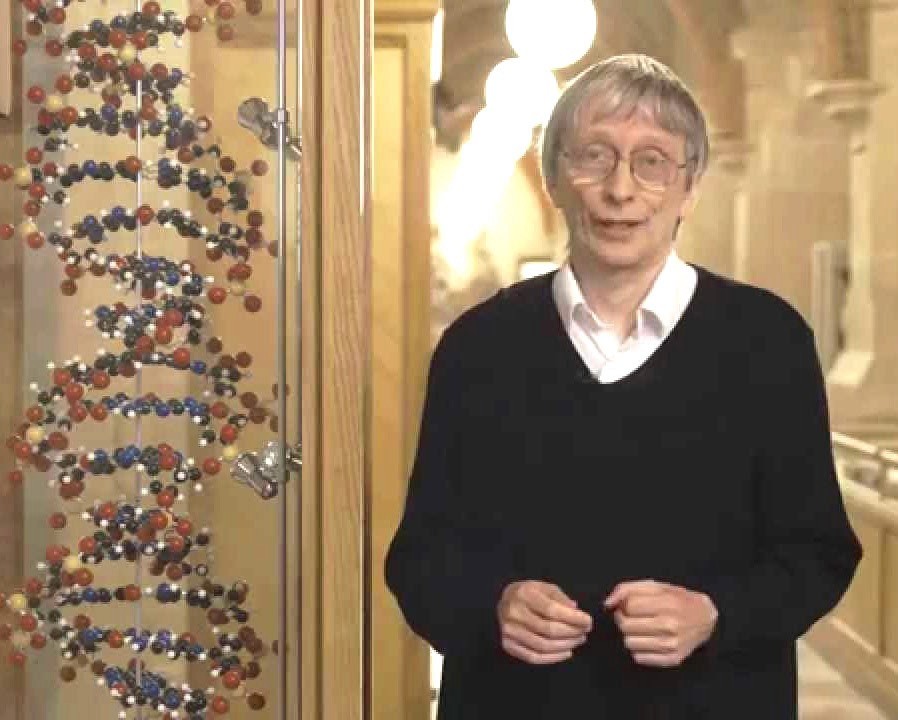

David Elieser Deutsch, often described as "father of quantum computing"
(Photo Credit: Wikipedia)
The field accelerated in 1994, when Peter Shor introduced an algorithm that could factor large numbers exponentially faster than classical machines, proving the extraordinary computational power of quantum mechanics. This led to the development of quantum error correction, which showed that reliable quantum computation was theoretically achievable despite noise. In 1996, Lov Grover introduced his famous Grover’s algorithm, which speeds up unstructured search from O(N) to O(√N), providing one of the most widely applicable quantum advantages. These breakthroughs transformed quantum computing from a theoretical idea into a credible scientific and technological discipline.
How does Quantum Computer Work? What’s Qubit?
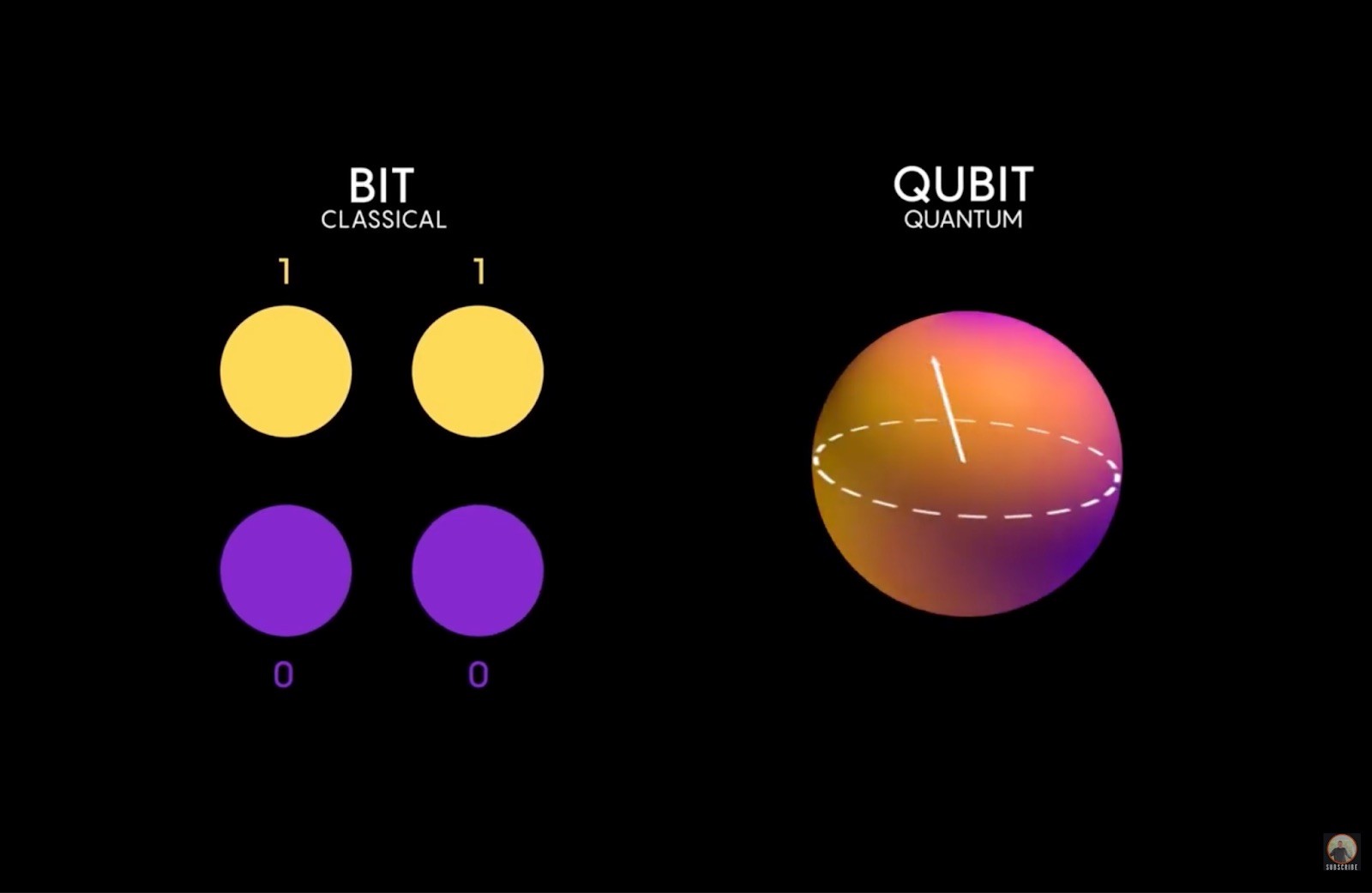
The fundamental unit of quantum information is the qubit (quantum bit).
Classical Computers use Bits: A light switch is either On (1) or Off (0).
Quantum Computers use Qubits: Due to a principle called Superposition, a qubit can be in a state of 1 and 0 simultaneously. Think of a coin spinning in the air; it is both heads and tails until it is observed.
A key difference is Scaling:
Classical:
1 bit = 1 state
100 transistors = 100 bits
Quantum:
1 qubit = 2 states
2 qubits = 4 states
10 qubits = 1,024 states
50 qubits ≈ 1 quadrillion states simultaneously
1,000,000 qubits (PsiQuantum’s goal) = astronomical computational space
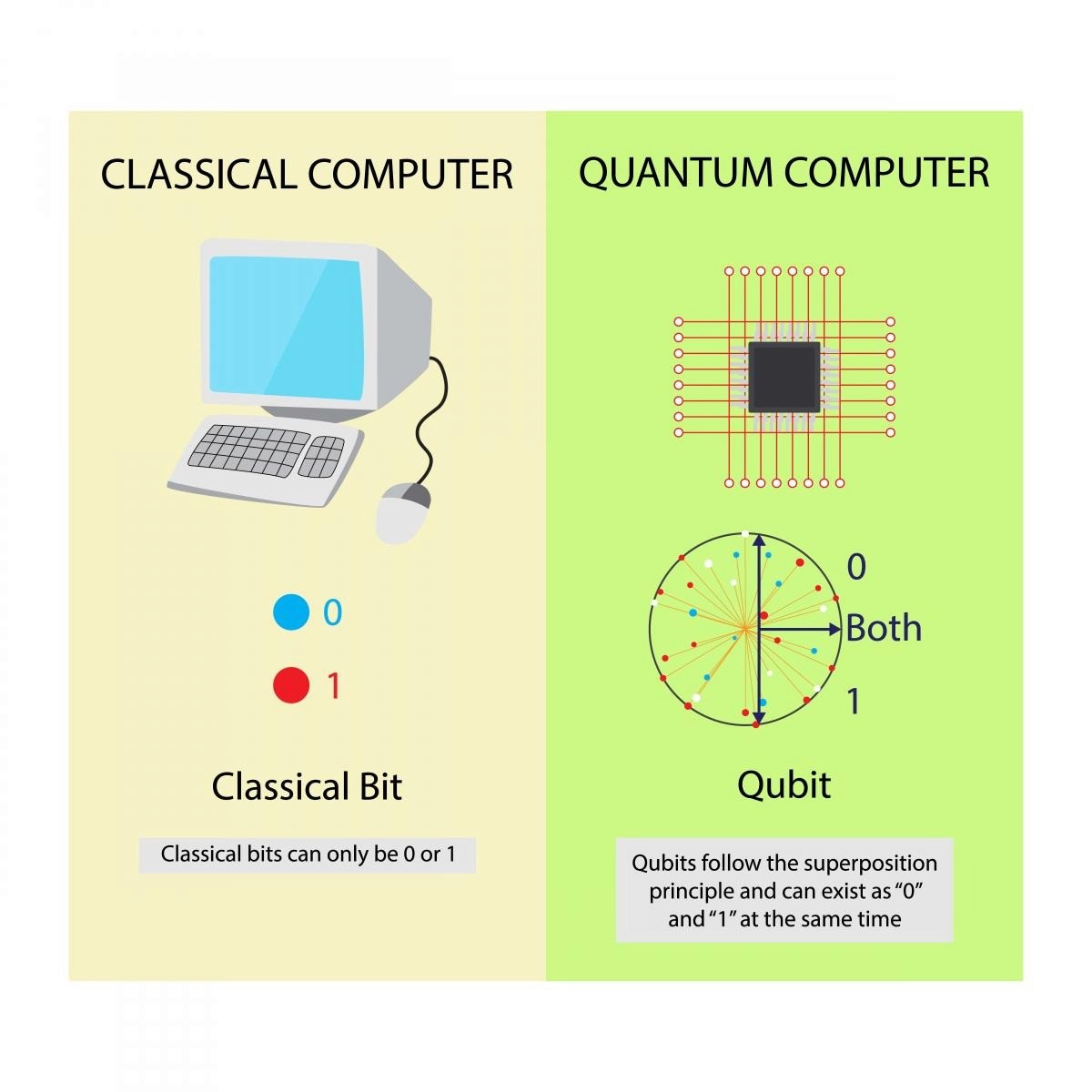
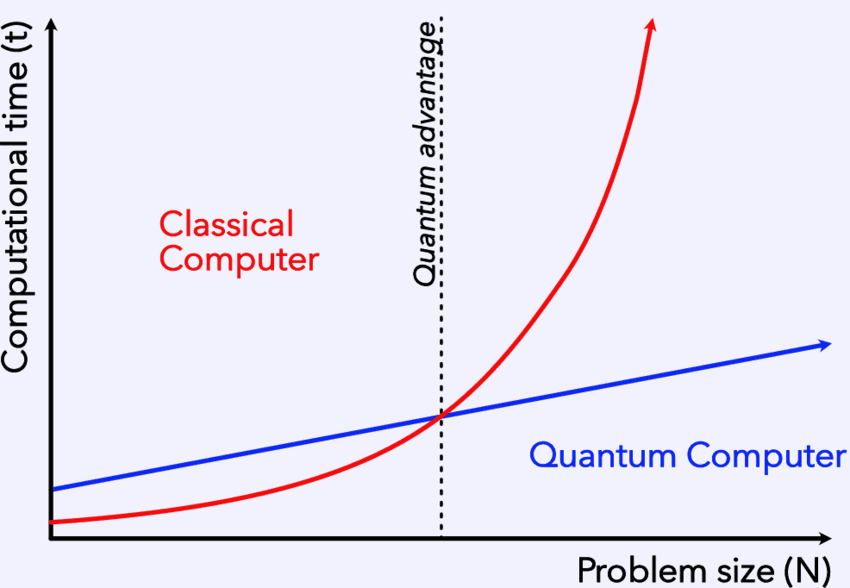
Photo Credit:berkeleynucleonics, researchgate.net
Key Quantum Features That Enable Quantum Computing
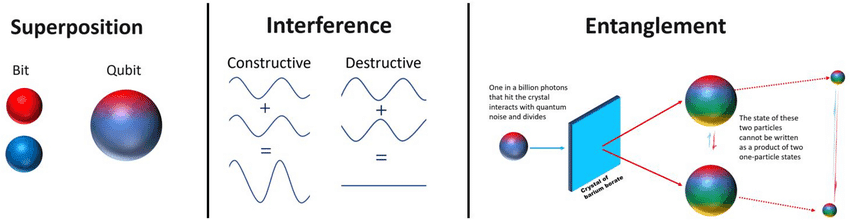
Quantum Features. Photo Credit: researchgate.net
Superposition allows a qubit to exist in a blend of multiple states simultaneously, rather than being strictly 0 or 1 like a classical bit. This means a quantum computer can represent and process many possible configurations at once. Superposition provides the massive parallelism that gives quantum computing its potential power.
Interference lets quantum states reinforce or cancel one another, like overlapping waves. Quantum algorithms use this to amplify correct answers and suppress incorrect ones.
Entanglement links qubits so that the state of one instantly relates to the state of another, even at a distance. This creates powerful correlations that enable multi-qubit operations and large-scale quantum processing.
Quantum Computing Approaches
There are a couple of approaches in the field of quantum computing, among them the main ones are as follows:
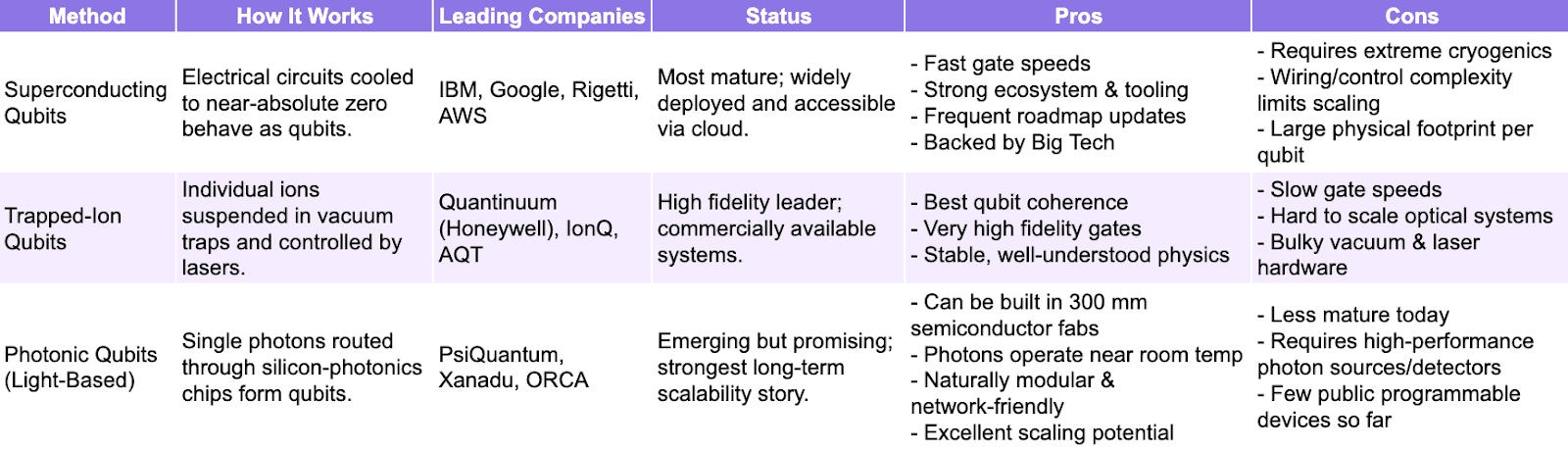
Copyright © Jarsy Research
PsiQuantum’s Advantage
Now, let's explore the strategy of PsiQuantum, the company that is deliberately forging a path outside the two established camps. PsiQuantum's "secret sauce" is Silicon Photonics, where optical components are integrated onto silicon chips using high-volume, standard manufacturing processes.
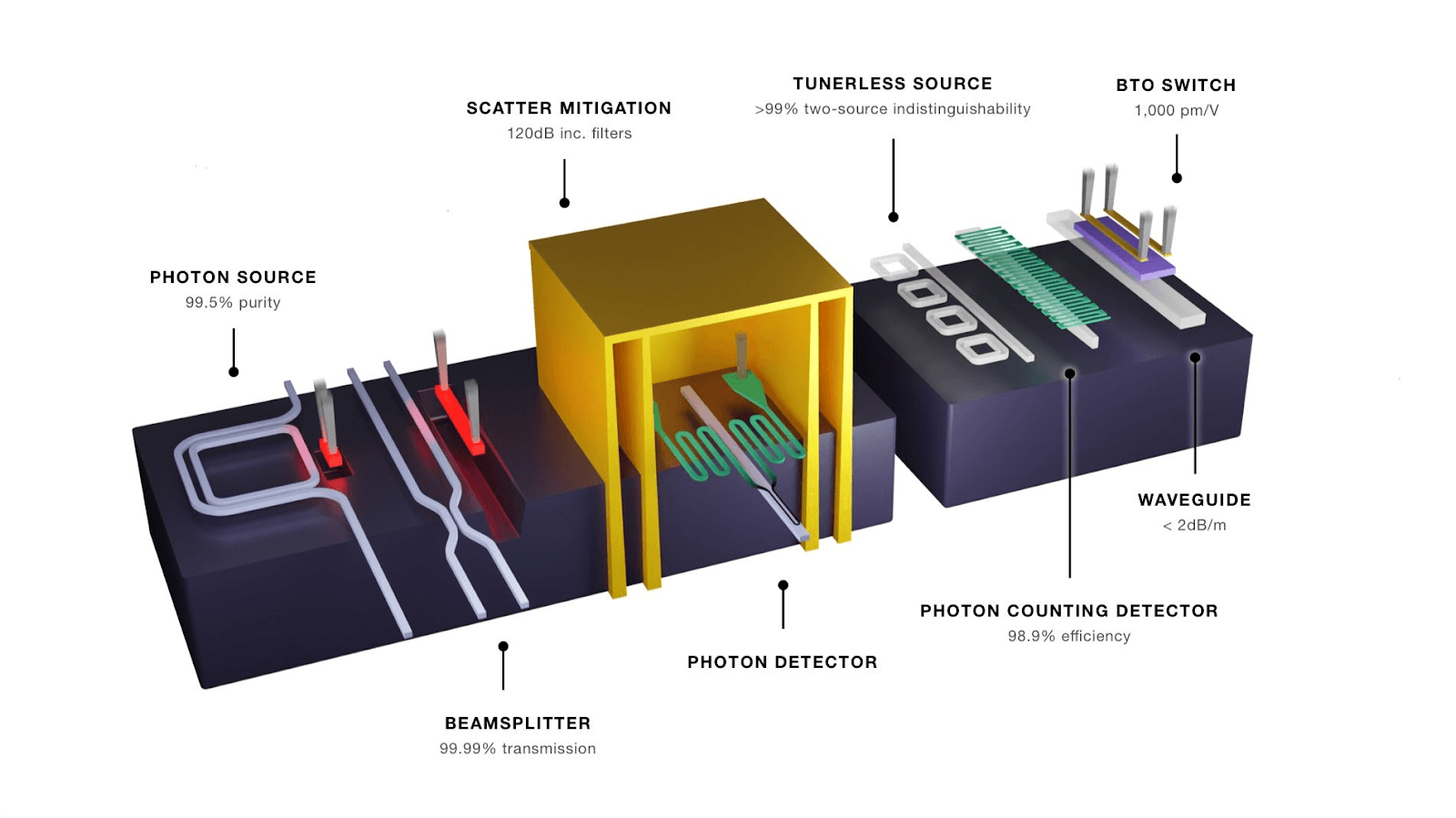
Photo Credits: PsiQuantum
Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) Manufacturing: PsiQuantum chips are printed in standard 300mm semiconductor foundries (like GlobalFoundries). This leverages the reliability and precision of a trillion-dollar industry that already manufactures billions of chips annually.
Room to Scale: This approach is inherently scalable. PsiQuantum is designed to print millions of qubits per wafer, addressing the biggest bottleneck in the industry: scaling past 100 or 1,000 qubits.
Robust Networking: Unlike the fragile connections required by other methods, photonic chips can be networked using standard, low-loss optical fiber, simplifying the connection of thousands of chips into a single, massive machine.
PsiQuantum’ Trillion-Dollar Use Cases – Fault Tolerance (FTQC)
The computers available today are Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) devices. Their high error rate limits them to experimental proof-of-concept.
PsiQuantum is skipping the NISQ era entirely to focus on a Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computer (FTQC).
The Necessity of FTQC: Error correction requires hundreds, sometimes thousands, of unreliable physical qubits to create a single stable, "logical" qubit. This means commercial utility demands systems with millions of physical qubits.
The Difference: An FTQC is the difference between a prototype that works half the time and a reliable, commercial product that can run complex algorithms for hours without crashing. PsiQuantum’s manufacturing-first model is designed to deliver this sheer scale.
If PsiQuantum successfully delivers an FTQC, the economic returns will be enormous. McKinsey estimates the market could unlock up to $2 trillion in value across four major sectors by 2035.
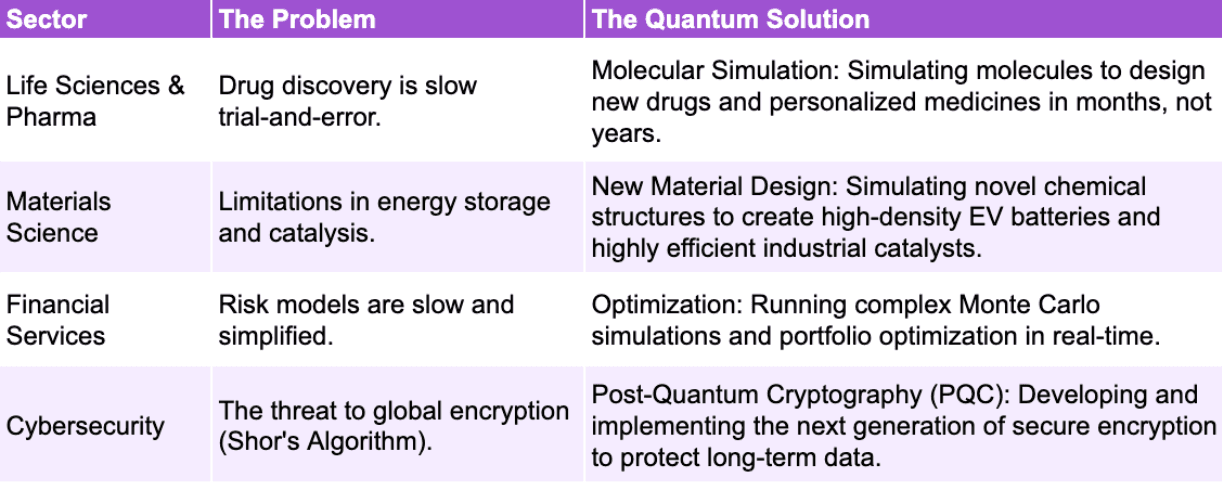
Copyright © Jarsy Research
Quantum computing is transitioning from scientific curiosity to an engineering challenge, and the race now centers on which approach can truly scale. PsiQuantum’s photonic strategy stands out because it leverages the existing semiconductor manufacturing ecosystem, turning quantum computing into something that can be built, replicated, and eventually deployed at industrial scale. There’s still a long way to go, but momentum is accelerating. Whether photons ultimately win or not, PsiQuantum has reshaped the conversation about what it will take to build a practical, fault-tolerant quantum computer. The next few years will be pivotal.
Further reading: Core Memory Video on PsiQuantum, Pete Shadbolt at Chicago Quantum Summit, A Beginner’s Guide to Quantum Computing, 3Brown1Blue on Quantum Computing