SpaceX: A Once-in-a-Generation Company
Founded by Elon Musk, the brilliant, relentless, occasionally outrageous entrepreneur of this era, SpaceX has grown from an audacious startup into one of the most influential aerospace companies in history. Long known for redefining the economics and cadence of spaceflight, the company is now drawing even greater global attention after Musk confirmed that a SpaceX IPO is targeted for 2026, a milestone investors have speculated about for years!
In just two decades, SpaceX evolved from a scrappy upstart blowing up early prototypes on a remote Pacific island to the most capable and influential space company on Earth. It changed how rockets are built, launched, reused, and priced. It built the world’s largest satellite constellation. And it reshaped the strategic landscape for governments, corporations, and entire industries.
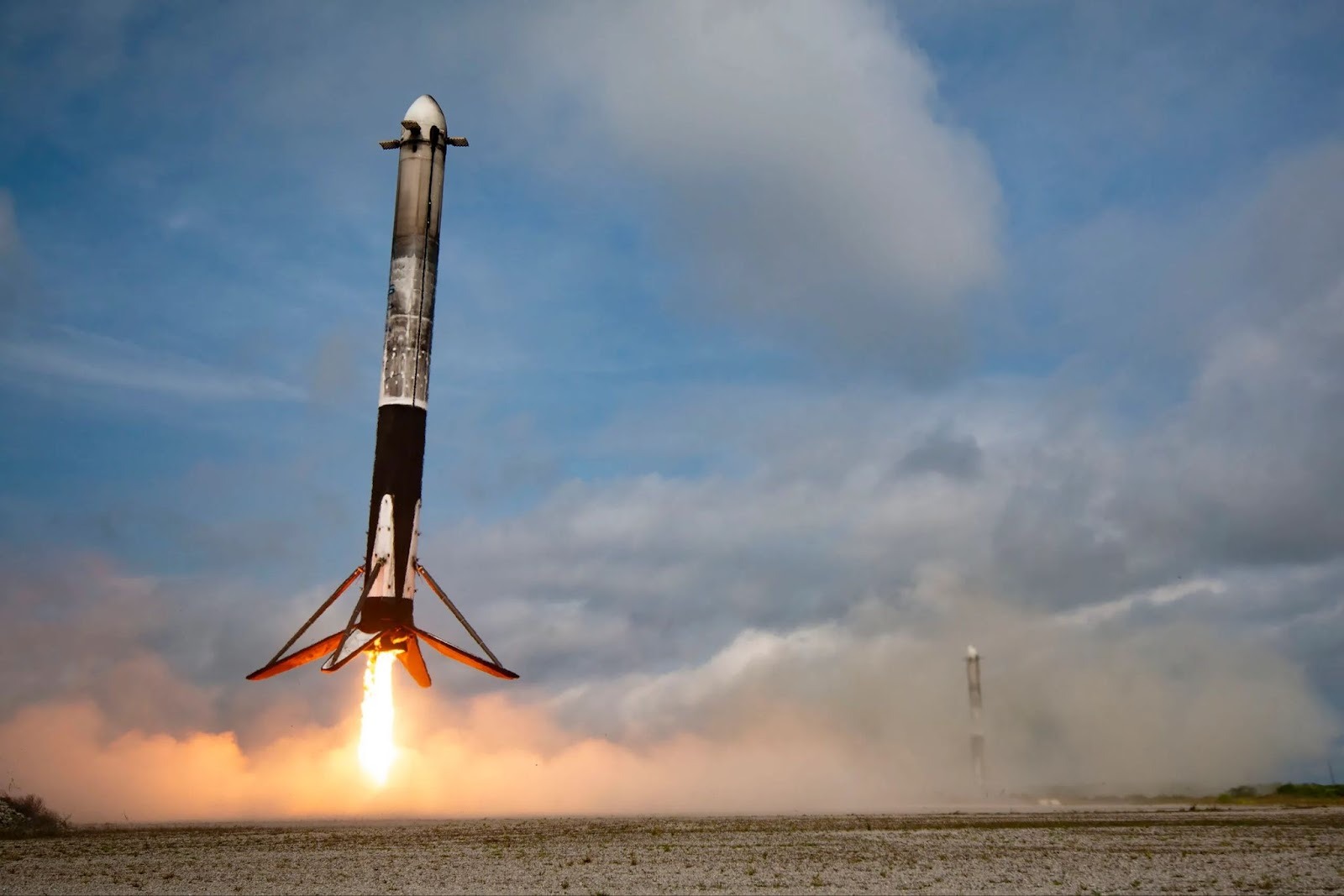
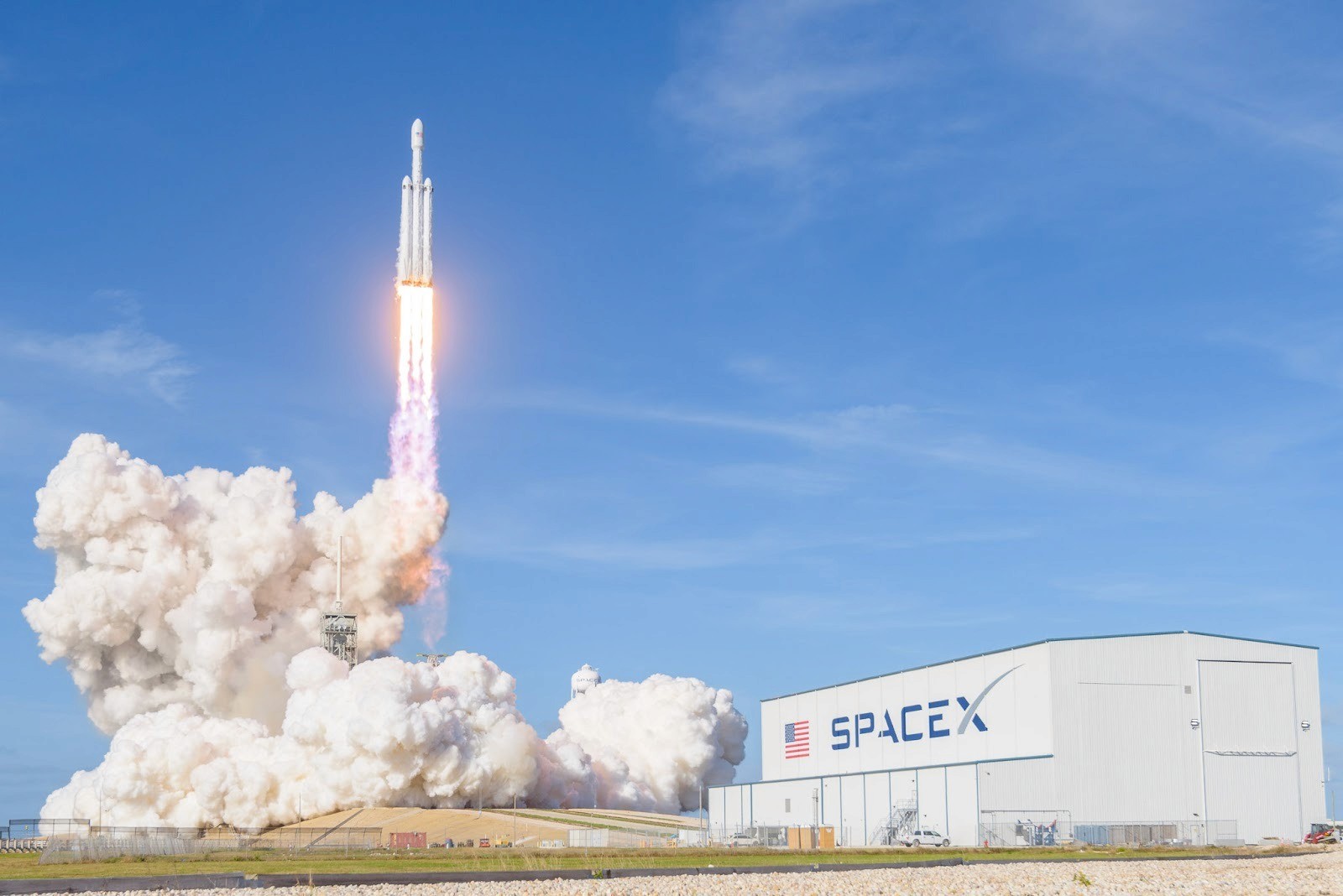
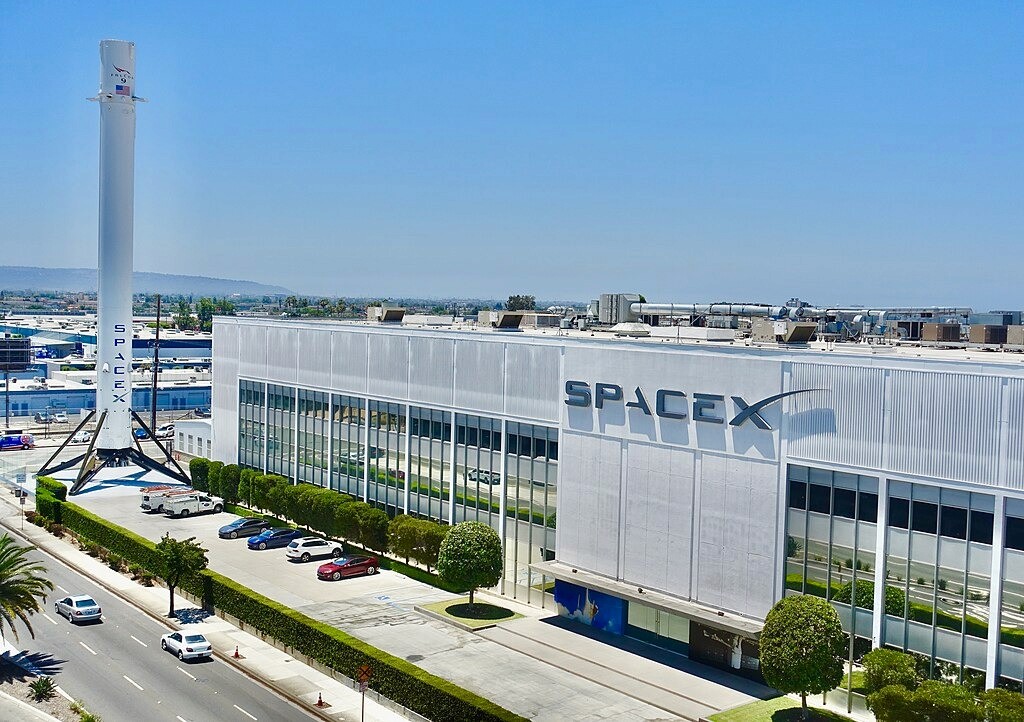



Image Credits: NASA, SpaceX, Wikipedia.org
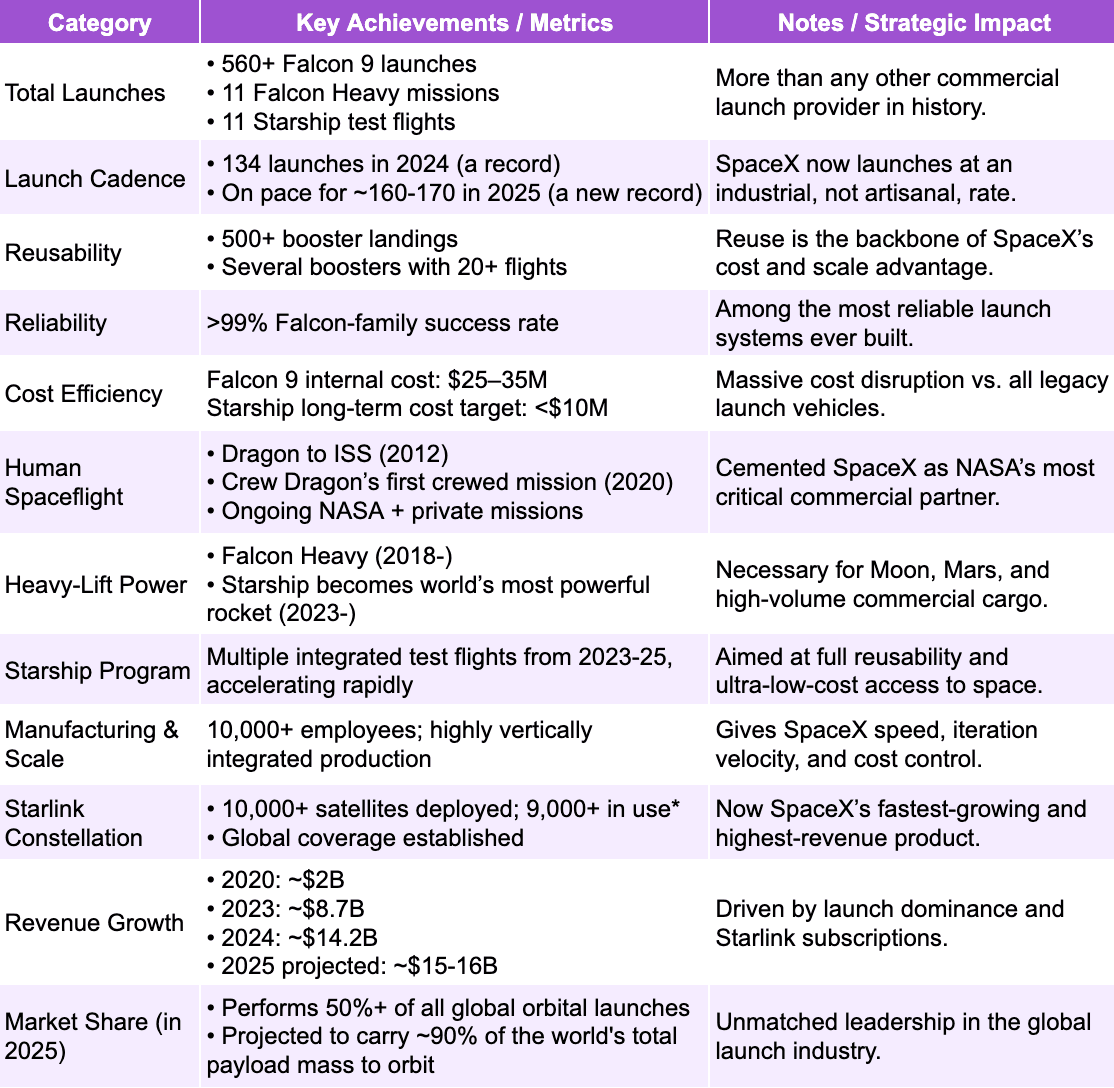
SpaceX’s rise is often summarized through its major technical breakthroughs: Falcon 1’s first orbital success (2008), Falcon 9’s debut (2010), Dragon’s first ISS cargo mission (2012), the first successful Falcon 9 booster landing (2015), Falcon Heavy’s twin-booster demo landing (2018), the first operational Starlink launch (2019), and Starship’s first full-stack test flight (2023). But each achievement reflected a deeper strategic shift:

Image Credits: LA Times, SpaceX Youtube Channel
Vertical Integration: Instead of outsourcing critical systems, SpaceX designed and built the majority of its hardware in-house.
Rapid Iteration: A software-like approach to hardware: build fast, test fast, fly fast.
Economies of Scale: By flying more often, SpaceX drove per-launch costs down while capturing more market share.
Before diving into Starlink, it’s worth looking at the milestones that made it possible:
Copyright © Jarsy Research
Starlink: From Side Project to SpaceX’s Core Business
The idea of Starlink was generated in 2015, when SpaceX began exploring how a vast constellation of low-Earth-orbit satellites could bring affordable, high-speed internet to parts of the world that traditional networks had never reached.
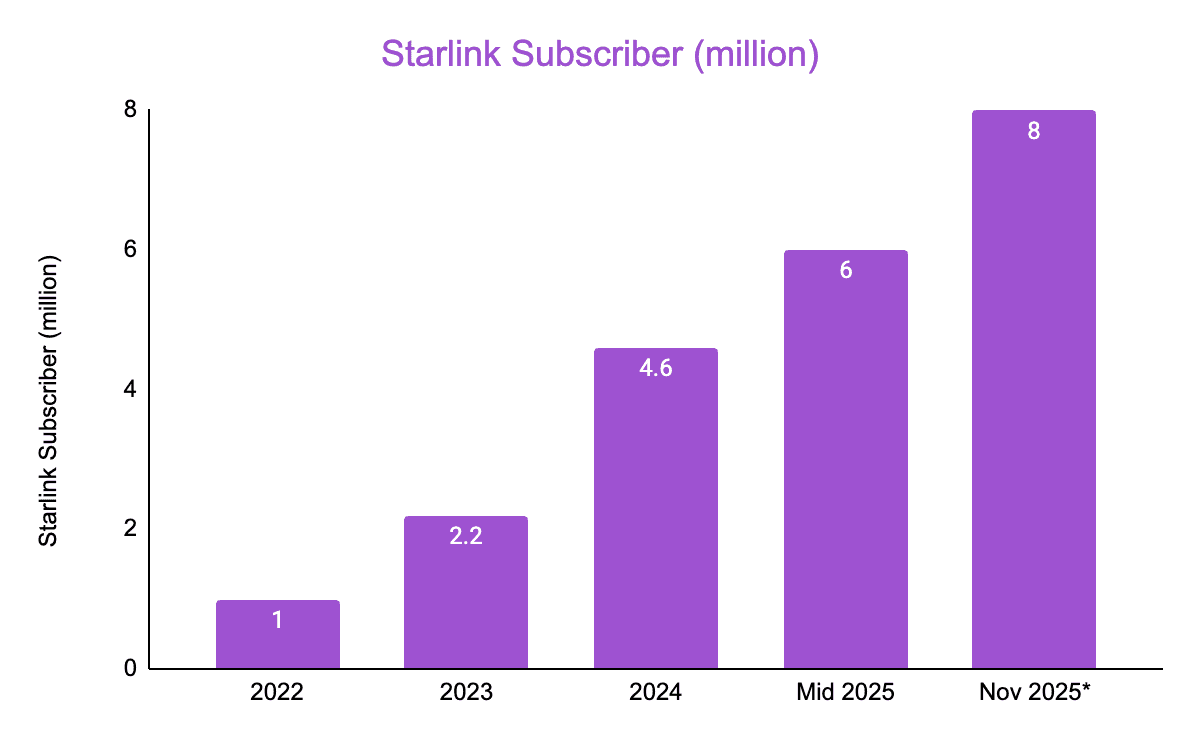
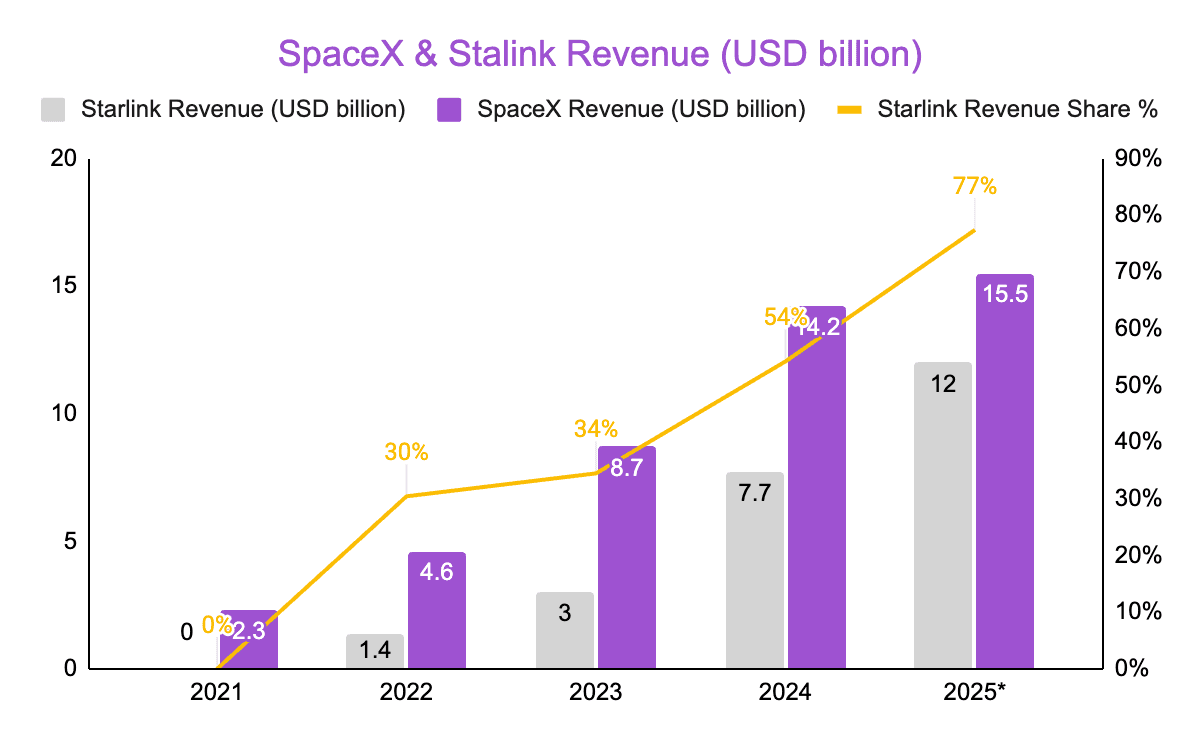
After securing key FCC approvals and launching test satellites in 2018, Starlink deployed its first operational batch in 2019 and opened a public beta in 2020, at the time serving only a few tens of thousands of early users. From there, growth accelerated rapidly: subscriber numbers climbed past 100,000 in 2021, exceeded 1 million by the end of 2022, and continued rising to more than 8 million users across 150+ countries by Nov 2025, spanning homes, businesses, aircraft, ships, and vehicles. Revenue followed a similar trajectory, growing from under a billion dollars in 2021 to more than 10 billion by 2025, making Starlink one of the fastest-scaling communications services in history. Beyond traditional internet service, Starlink also enables cellular backhaul and is developing direct-to-cell connectivity, allowing standard smartphones to connect directly to satellites. SpaceX has expanded the platform with Starshield, a secure government-focused variant designed for national security, defense, and resilient communications.
And as of Dec 11, 2025, there are 9,149 starlink satellites active in Lower Earth Orbit according to satellitemap.space (see the first photo in the newsletter).
*2025 data are estimated. Copyright © Jarsy Research
How Starlink Works: The LEO Advantage
Starlink works by operating a three-layer network consisting of thousands of low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites, user terminals (dishes) on the ground, and a global system of ground gateways that link the constellation to the internet.
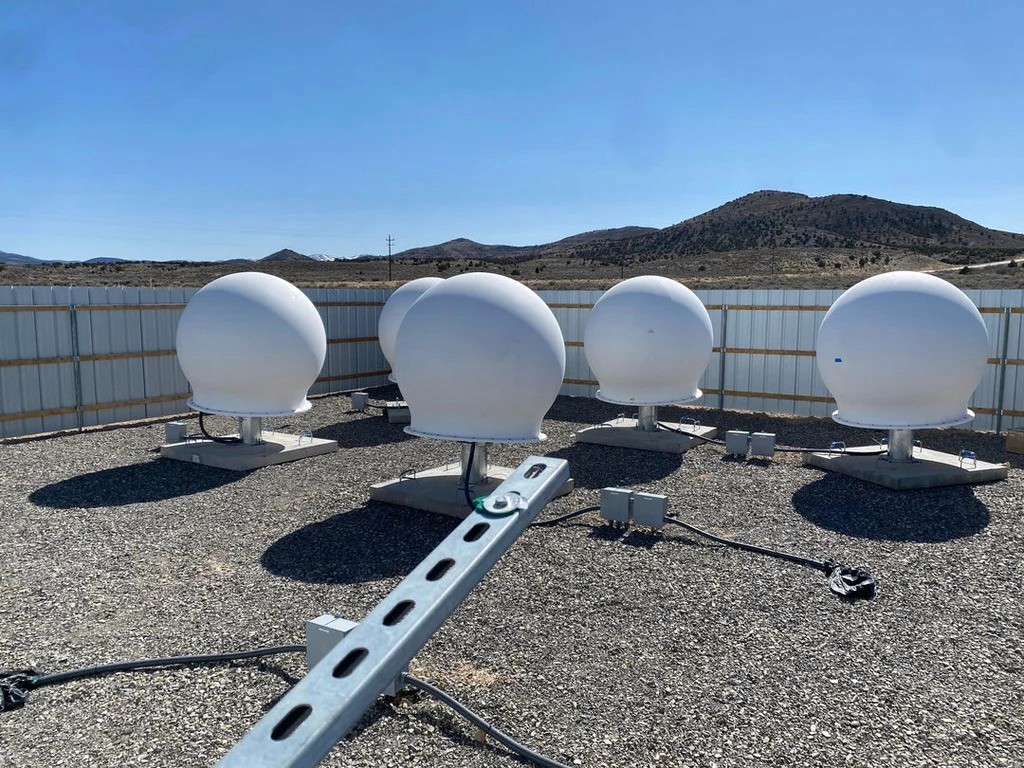
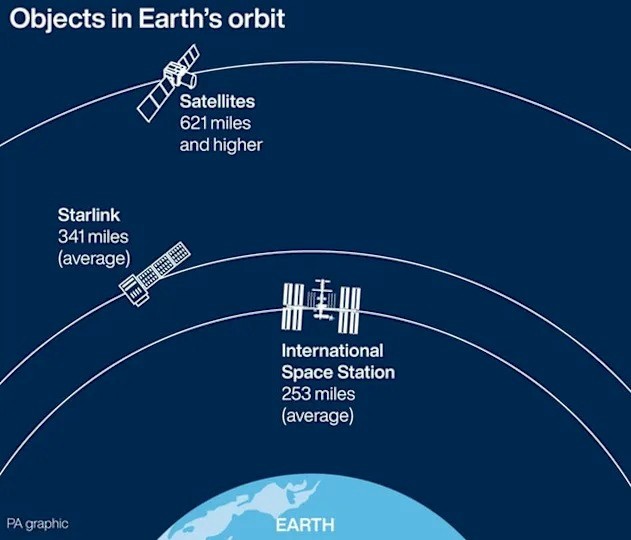
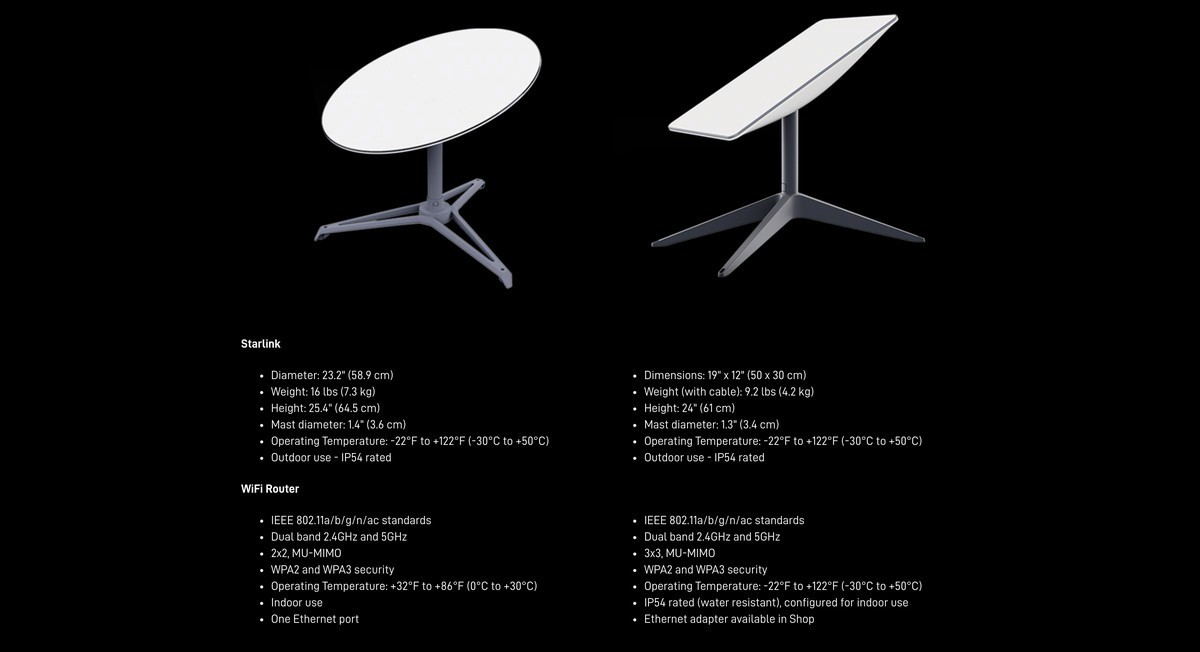

Image Credits: Yahoo Finance, Starlink, starlinkinstallationpros.com
Because the satellites fly in LEO, only a few hundred kilometers (around 550 km) above Earth rather than 36,000 km like traditional geostationary satellites, signals travel far shorter distances, giving Starlink a key advantage: dramatically lower latency, often similar to fiber connections. A user terminal automatically tracks the satellites overhead with an electronically steered antenna, sending data up to the nearest satellite, which then routes it either down to the closest gateway or across space to another satellite via Intersatellite Links (Laser Links). These laser links allow satellites to pass data between one another at nearly the speed of light, creating a space-based backbone that can move information globally without needing ground stations beneath every coverage area, especially useful over oceans, remote regions, and disaster zones. As more satellites are added, this moving mesh of LEO spacecraft becomes denser and more resilient, enabling fast, consistent broadband service almost anywhere on the planet.
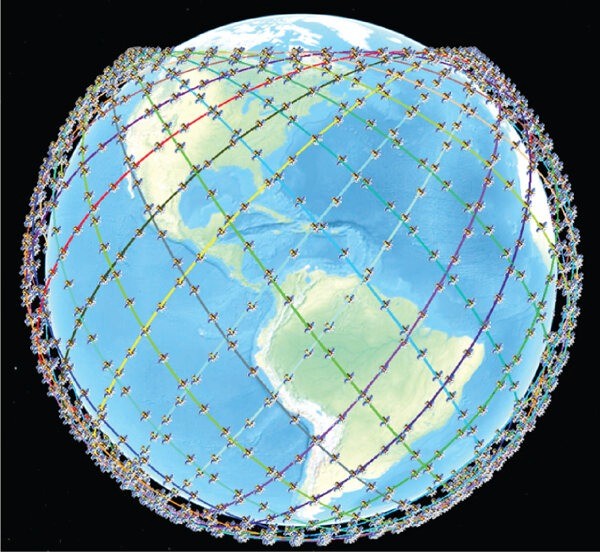
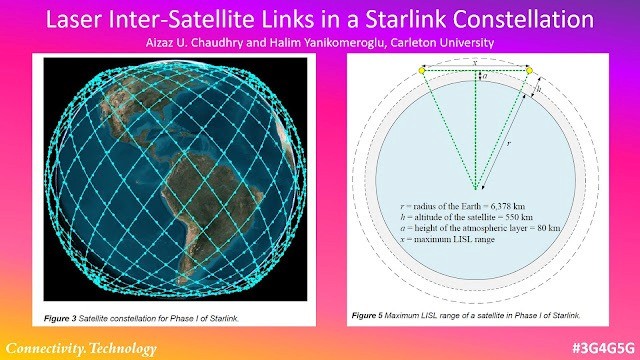
Image Credits: researchgate.net, connectivity.technology
Product Innovation
Starlink’s satellite technology has rapidly evolved through several generations, beginning with the lightweight v1 satellites that enabled the initial constellation and early beta service. These were followed by v1.5, which introduced intersatellite laser links and improved reliability, expanding coverage to remote and oceanic regions. In 2023, SpaceX rolled out the v2 Mini, a more advanced and heavier design featuring higher throughput, stronger laser links, and upgraded power and antenna systems, bridging the gap until the full-size v2 and future v3 satellites can be deployed aboard Starship. These upcoming generations are expected to deliver dramatically greater capacity, efficiency, and performance, supporting Starlink’s long-term vision of a high-bandwidth, globally resilient space-based internet network.
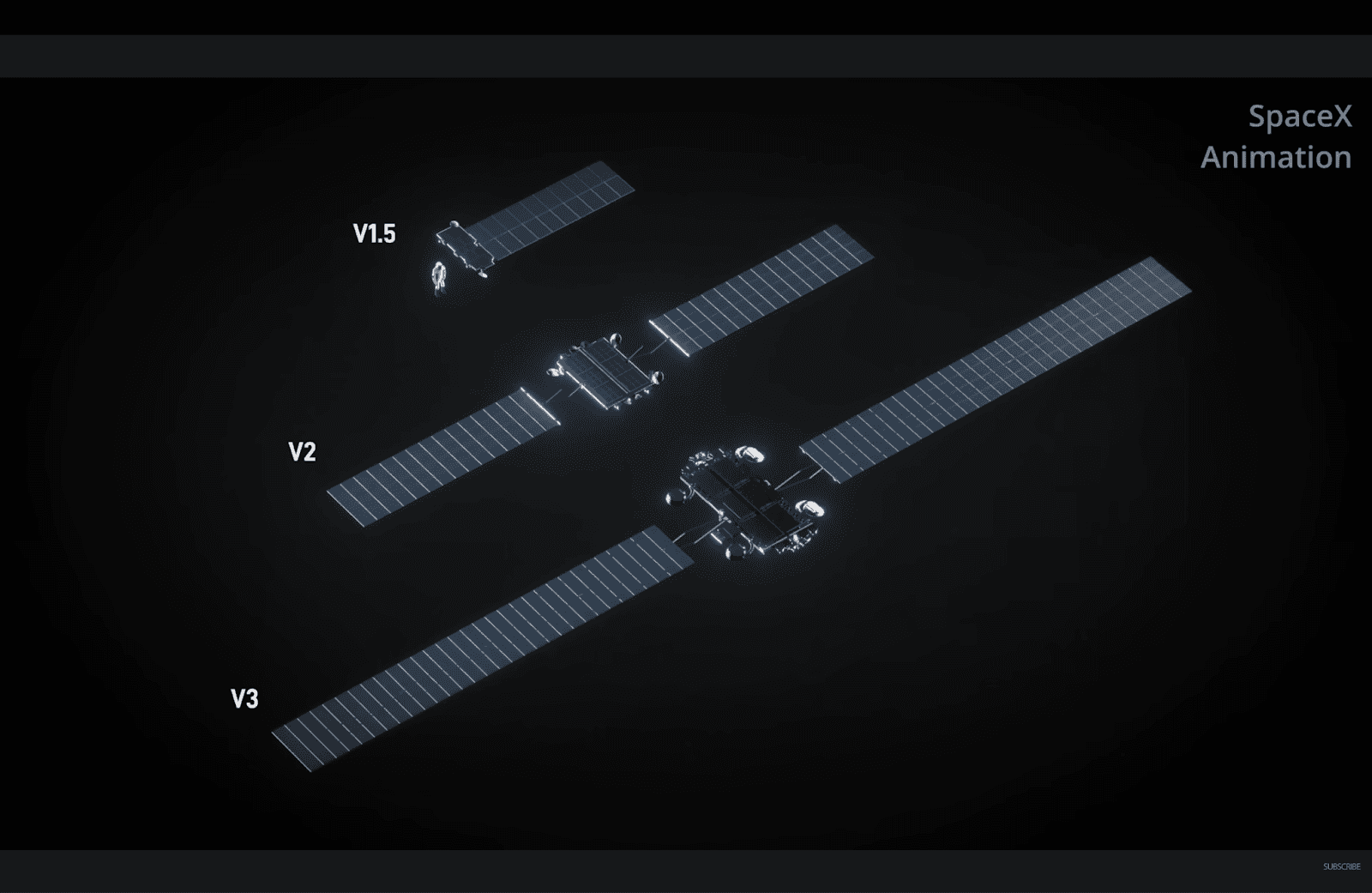

Image Credits: Starlink, Wikipedia
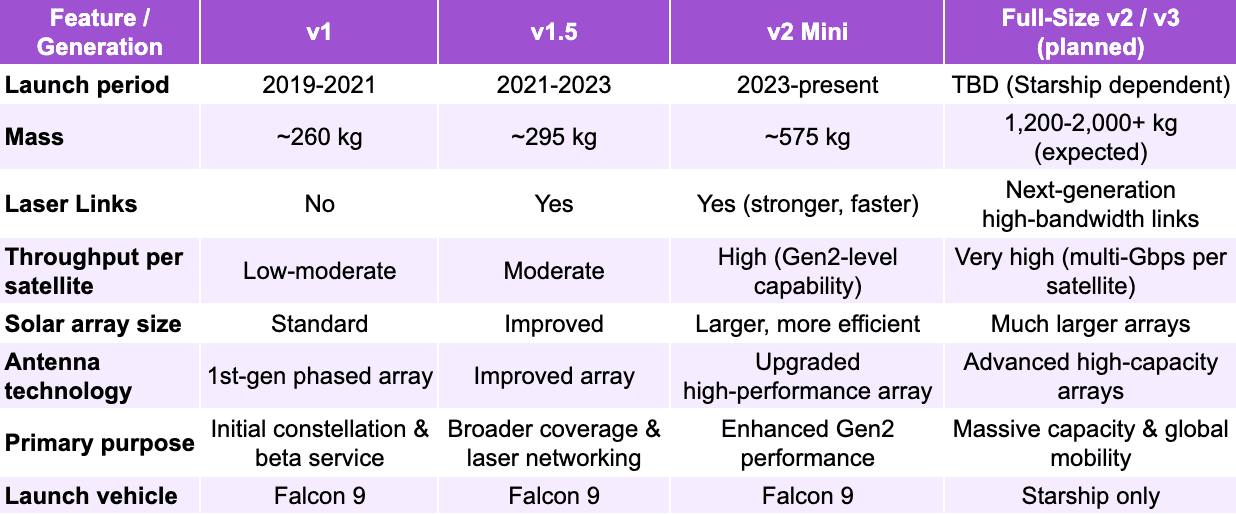
Copyright © Jarsy Research
Future AI Data Center
Recently, Elon mentioned the idea of “Satellites with localized AI compute,” describing a future where Starlink satellites do more than carry internet traffic: they host AI processing directly in space to bring compute closer to users and leverage abundant solar energy. This concept aligns with emerging research that explores scalable AI systems in orbit using fleets of satellites equipped with solar arrays, inter-satellite free-space optical links, and onboard accelerator chips like Tensor Processing Units (TPUs), designed to survive the radiation environment of low Earth orbit (LEO) over mission lifetimes.
The vision is to cluster satellites into tightly coordinated, high-bandwidth formations capable of distributed machine learning tasks and low-latency inference, minimizing data transfers to and from Earth while tapping into constant solar power, a potentially transformational step toward space-native AI infrastructure.
Models in this class could build on future Starlink V2/V3-class platforms with large power budgets, advanced thermal systems, and high-capacity intersatellite networks, distinguishing them from more communications-focused generations like v1 and v2 Mini, which are optimized for broadband traffic rather than heavy compute. Google’s Research suggests that launch costs to LEO may approach $200-300/kg by the mid-2030s ($810–7,500/kW/y), a threshold that makes deploying space AI clusters economically plausible when balanced against Earth-based data center costs ($570–3,000/kW/y) and the advantages of orbit for certain inference workloads.
If realized, space-based AI compute could open new revenue streams for SpaceX and Starlink by serving edge AI demands across global networks, though concrete market forecasts will depend on adoption rates, regulatory environments, and how rapidly space launch economics improve.
SpaceX Valuation and Future Growth Projections
Thanks to Starlink’s rapid growth, SpaceX’s valuation has risen remarkably: from under $15 billion in 2015, to around $100 billion by 2021, passed $300+ billion in 2023, and now rumored at $800+ billion! Looking ahead, institutions see potential for much larger gains. ARK Invest projects SpaceX could reach roughly $2.5 trillion by 2030, while other analysts suggest a possible 2026 IPO could come in between $800 billion and $1.5 trillion, depending on Starship’s progress and Starlink’s continued expansion.
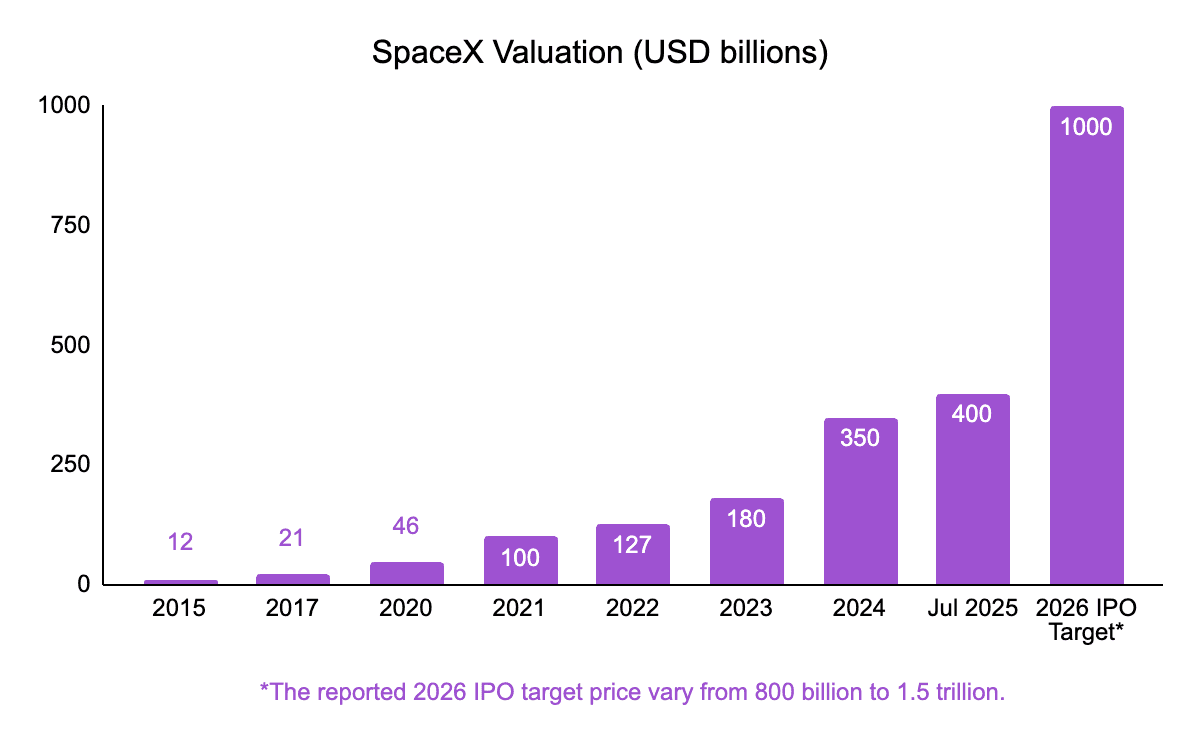
Copyright © Jarsy Research
Starlink and SpaceX have reached a moment where their early ambitions are turning into globally scaled infrastructure. What began as a push for reusable rockets and universal internet access has grown into a platform for mobility, defense, and future space-based computing. With Starship poised to accelerate deployment and enable entirely new classes of satellites, the roadmap ahead stretches well beyond today’s capabilities. The full impact of this system is still unfolding, and its long-term potential is likely far greater than anything we can predict. How far it ultimately goes, perhaps only the stars will know! :)

Image Credit: SpaceX Youtube Channel
Further Read: Google's Research Paper, Falcon Heavy's double landing, ARK's 2030 SpaceX Valuation